Generative AI has sparked a new wave of productivity, and with it, a new category of security risk.
As AI tools and platforms become more accessible and powerful, employees are adopting them without IT oversight. In fact, our 2025 State of Data Security Report revealed that 98% of employees use unsanctioned apps across shadow AI and shadow IT use cases.
While it may seem harmless, shadow AI can expose your sensitive data, undermine compliance and introduce unseen vulnerabilities into your environment. In this article, you’ll learn what shadow AI is, why it’s risky for enterprises and how to address it without stifling innovation.
What is shadow AI?
Shadow AI refers to the use of artificial intelligence tools and applications by employees without formal approval or governance from their IT departments. Much like shadow IT, shadow AI specifically involves generative AI models, agents, copilots, tools, and other AI systems that haven’t undergone proper security vetting processes.
With the explosive growth of user-friendly AI platforms, employees can easily access powerful AI capabilities. The sheer convenience, cost-effectiveness, advanced features and open-source nature of AI tools make them alluring to any employee looking to boost their productivity, but it comes with substantial hidden risks. The US Congress’ recent banning of Deepseek put a spotlight on shadow AI’s critical security concerns.
The growing security threat of shadow AI
The security implications of shadow AI extend far beyond typical software risks. Employees who input corporate data into unauthorized AI systems may inadvertently expose sensitive information to external entities with unclear data handling practices.
Here’s what you should look out for when determining how your data is handled by AI platforms:

Data processing concerns
Let’s examine the popular AI platform DeepSeek. According to its privacy policy, DeepSeek processes user prompts on servers located in China.
This means:
- All data submitted to the platform is subject to Chinese data privacy laws and regulations
- Organizations may face compliance issues with U.S. regulatory requirements
- Sensitive information could be processed outside your organization’s security perimeter
- Data sovereignty becomes a significant concern for regulated industries
While developers can host DeepSeek local instances on walled-off servers, many employees simply use the publicly available version without considering these implications.
Sensitive information exposure
Say, for example, a sales representative pastes a client contract into an AI tool to help summarize key points for a meeting. Without realizing it, they’ve potentially exposed confidential pricing structures, client information and proprietary terms to servers outside the company’s control. This data could be incorporated into the AI’s training data or accessed by unauthorized parties.
The act itself sounds innocent enough, but this type of inadvertent data leakage represents one of the most significant risks associated with shadow AI.
Why traditional bans don’t work on shadow AI
Many organizations addressed shadow AI by implementing bans on tools like DeepSeek. Governments and entire countries like Italy have taken steps to block certain AI platforms to protect against shadow AI risks.
Traditional corporate bans, however, have proven difficult to enforce for several reasons:
- Employees find workarounds when they believe AI will help with productivity
- Personal devices and home networks provide alternative access points
- The growing number of AI tools makes comprehensive blocking impractical
- Employees may not understand the security implications of their actions
Join us for our next webinar, Shining a Light on Shadow AI.
The unique challenge of open-source AI
Unlike concerns about applications like TikTok or hardware from companies like Huawei, open-source AI tools present different security challenges.
Open-source models:
- Enable cybercriminals to launch massive campaigns more efficiently due to their low cost to train and run
- Create challenges for organizations looking to identify when and how these tools are being used
- Has code that can be modified and deployed in ways that evade detection
- Increase vulnerability to targeted attacks due to open-source models’ transparency
Effective shadow AI risk mitigation strategies
It’s not all doom and gloom; organizations can still reap the benefits of AI. Rather than blocking or banning all AI tools, organizations can implement these strategies to manage shadow AI risks while leveraging AI’s benefits.
Develop clear AI policies
Organizations can start mitigating AI risk by establishing and communicating clear guidelines about approved AI tools and usage.
Typical policies include:
- Create specific protocols for handling sensitive information
- Define consequences for unauthorized AI tool usage
- Establish clear channels for requesting access to new AI tools
- Update data classification policies to account for AI-specific risks
For example, a marketing team might develop guidelines that allow the use of approved AI tools for brainstorming campaign concepts but require human review before implementing any AI-generated content.
Offer secure alternatives
When employees turn to shadow AI, it often indicates they need capabilities not provided through official channels.
To combat this, organizations should:
- Consider building isolated instances using open-source code
- Evaluate enterprise-grade AI solutions with proper security controls
- Implement walled-off versions that don’t connect to external servers
- Create internal AI sandboxes where employees can experiment safely
Software development teams, for example, can benefit from internally hosted coding assistants that help with tasks without exposing proprietary code to external AI platforms.
Prioritize employee education
Many shadow AI risks stem from a lack of awareness rather than malicious intent. It’s the responsibility of organizations looking to implement AI to:
- Educate staff about data security risks associated with AI tools
- Provide clear alternatives to unauthorized AI apps
- Explain the implications of sharing sensitive information with AI models
- Create simple decision frameworks for when AI use is appropriate
Implement technical controls
Technical solutions offer strong capabilities in managing shadow AI. To secure their environment for AI, organizations can:
- Deploy Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tools to identify sensitive data being shared with AI platforms
- Use DNS and web proxy monitoring to detect unauthorized AI usage
- Implement least privilege access to minimize potential exposure
- Regularly audit application integrations to identify shadow AI tools
Enabling shadow AI innovation, but with security
The key to managing shadow AI effectively in an organization lies in balancing enabling innovation and maintaining security. Finding this balance means:
- Creating clear pathways for employees to request new AI capabilities
- Establish risk assessment frameworks specifically for AI tools
- Regularly review and update AI policies as the technology evolves
- Involve business units in AI governance decisions
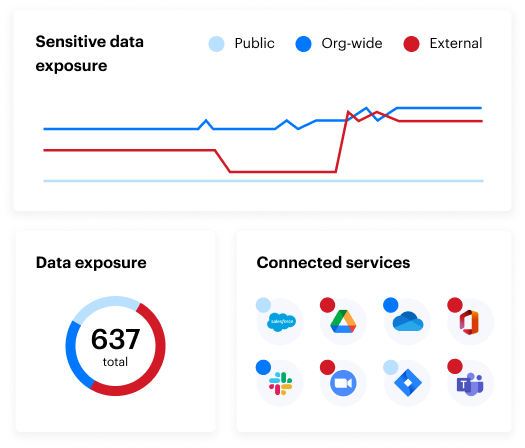
Discovering and managing shadow AI with Varonis
Specialized tools like Varonis enable organizations to identify shadow AI usage and address its challenges through features like:
- Network monitoring capabilities that detect AI tool usage through DNS and web proxy logs
- SSPM functionality that automatically identifies and removes shadow AI apps and plugins integrated into sanctioned SaaS applications without IT approval
- User activity tracking to determine which employees installed AI apps, when they did and what actions were performed
- Data discovery and classification tools that can identify files, source code, emails and other content related to unauthorized AI tools
Interested in learning more about your organization’s data security posture? Take our free Data Risk Assessment.
The hidden risks of shadow AI: FAQs
What is shadow AI?
Shadow AI refers to employees using artificial intelligence tools and applications without formal approval or governance from IT departments. Similar to shadow IT, where employees adopt unauthorized software or hardware, shadow AI specifically involves generative AI models, machine learning tools and other AI systems that haven’t gone through proper security vetting processes
What are the risks of shadow AI?
The risks of shadow AI include:
- Exposure of sensitive corporate data to external entities with unclear data handling practices
- Compliance issues with regulatory requirements when data is processed in different jurisdictions
- Data sovereignty concerns for regulated industries
- Inadvertent leakage of proprietary information
- Potential processing of company data on servers with unknown security controls.
What are examples of shadow AI?
An example of shadow AI would be employees using tools like ChatGPT or open-source LLMs (such as DeepSeek) to write code, analyze data, generate marketing content or summarize customer contracts, all without IT approval or security review.
How can organizations detect shadow AI usage?
Shadow AI can result in non-compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA if sensitive data is processed in unauthorized or unregulated environments, especially across international borders.
How is shadow AI different from shadow IT?
Shadow AI is a subset of shadow IT focused explicitly on the unsanctioned use of artificial intelligence tools. While shadow IT includes any unapproved hardware or software, shadow AI introduces unique data privacy and model training risks.
What should I do now?
Schedule a demo with us to see Varonis in action. We'll personalize the session to your org's data security needs and answer any questions.
See a sample of our Data Risk Assessment and learn the risks that could be lingering in your environment. Varonis' DRA is completely free and offers a clear path to automated remediation.
Follow us on LinkedIn, YouTube, and X (Twitter) for bite-sized insights on all things data security, including DSPM, threat detection, AI security, and more.