This article is part of the series "Working With Windows Local Administrator Accounts". Check out the rest:
Before we delve into Restricted Groups, I thought it might be worthwhile to take a closer look at how hackers take advantage of Administrator passwords. For Pass-the-Hash fans, this post will show you how hashes can be used even with local accounts. I also had a chance to try Windows Local Administrator Passwords Solution or LAPS. Spoiler alert: LAPS scares me a little.
Passing Local Hashes
After writing the first post, I realized that you don’t necessarily need hashes of domain accounts. In fact, Windows also stores the hashes of local accounts in its Security Accounts Manager (SAM) database. Hash dumping tools such as crackmapexec and mimikatz let you view these hashes.
This leads to a more direct lateral movement tactic. As I pointed out last time, it is not unusual for local Administrator accounts to have exactly the same password on more than one machine. This would also mean the NTLM hashes would be the same as well.
Let’s say a hacker gains access to a server, and assuming he has enough privileges, then uses mimikatz to see if a local Administrator account is available. He can then try an experiment and pass the Administrator hash into, say, psexec to pop a shell on another server and gain Administrator privileges there as well.
Get the Free Pentesting Active
Directory Environments E-Book
You see what I’m getting at? If you assume that Administrator passwords are the same on different machines, then you’re no longer dependent on a domain-level user to have left a hash in the LSASS memory of that box. This post explains more about LSASS if you’re confused by the last sentence.
On the other hand, the local user hashes are always there! Being a hacker or pen tester means that you’re always testing different ideas and playing the odds. So let’s go for broke!
Back in my Acme domain, I set the same local Administrator password on both my Masa and Taco servers – Taco is also my domain controller. In this scenario, I’m already on Masa, I’ve uploaded mimikatz and psexec.
By the way, both these tools have source code, so it wouldn’t be that difficult to make them fully undetectable after a few tweaks.
I was now flying under the radar on Masa, but couldn’t find anything interesting there. To begin my lateral move, I loaded mimikatz and dumped the hashes with the lsadump::samcommand.
Assuming that Taco also has the same Administrator password, I then use sekurlsa:pth to launch psexec and gain a shell on Taco (below).
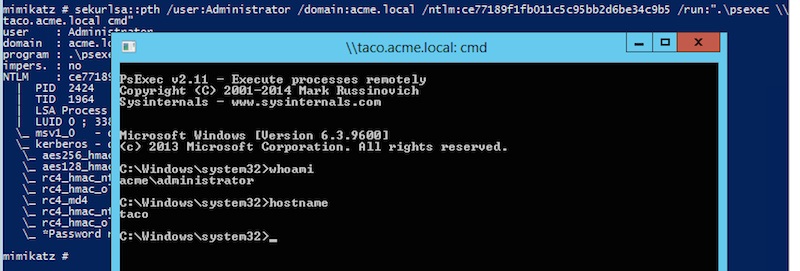
Amazing!
When I changed the Taco Administrator’s password, this ploy didn’t work, and psexec was unable to pop a shell.
Lesson learned: it’s good idea to have different Administrator passwords.
LAPS and Aspirin
If you’re going to keep the local Administrator passwords, then you need to manage them. As I wrote about last time, these accounts can be disabled, and Restricted Groups can be used to delegate Administrator privileges to domain-level accounts.
In any case, people still want these local accounts. Microsoft apparently heard the collective cry of IT administrators, and in 2015 they released their Local Administrator Passwords Solution. It’s described with these words: “…solution to the issue of using a common local account with an identical password on every computer in a domain. LAPS resolves this issue by setting a different, random password for the common local administrator account on every computer in the domain.”
Seems simple. However as we’ve noted before, Microsoft never, ever does anything nice and easy.
The first tip off was the LAPS architecture (see below).
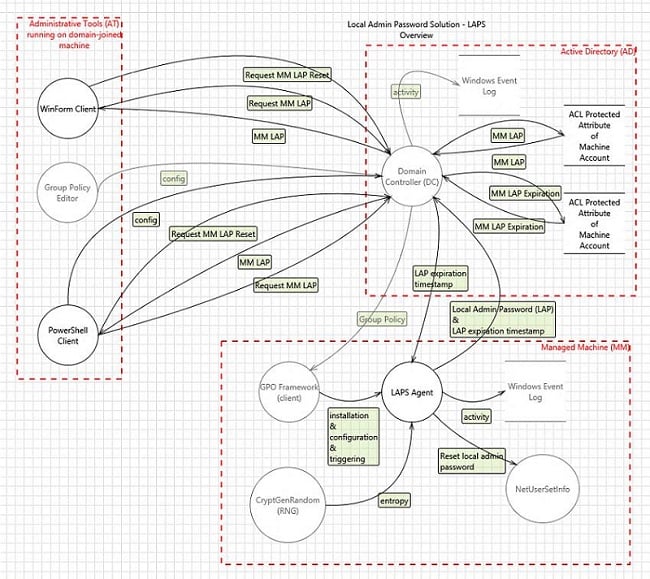
Hmm, there is a client and server side to this. The documentation also indicates PowerShell scripts have to be run, and then there’s something about changing the Active Directory schema.
I boldly took the LAPS challenge and went as far as I could with the installation before the pounding in my head got to me.
This is not an easy install. LAPS is loaded onto your domain controller as well as on client computers that you want managed. Yeah, you use the Group Management Console to push out LAPS to the clients.
If you do the installation correctly, you’ll see the following interface pop up when you navigate in the GPO editor to Computer Configuration>Administrative Templates>LAPS.
I was afraid to pull the trigger on this. In theory, LAPS generates random passwords that are now centrally located on Active Directory in a new attribute as plaintext — that’s why you needed to update the AD schema.
Some security pros have pointed out that LAPS may, ahem, have its own problems. Essentially, you’re shifting the problem from local computers to Active Directory.
Back to Restricted Groups
After returning from my LAPS detour, I began to see Restricted Groups as the most practical way to manage local Administrator accounts. I started on this process in the previous post when I created a new AD group called Acme-IT, which then was pushed out and placed under the local Administrators group for each machine in the Acme domain
It’s a neat trick, and Restricted Groups allow IT to centrally control local Administrator access.
It would even be neater if I could segment my domain so that one group of users would be local Administrators for a subset of machines, and another group would control a different subset –creating as many sub-groupings as needed.
Otherwise, I’d fall into the trap of allowing a small group of users to have local Administrator access to the entire domain! No bueno.
And that’s where Organizational Units (OUs) come into play. It’s a way to divide up the domain so that you can associate specific GPOs with each OU subgroup.
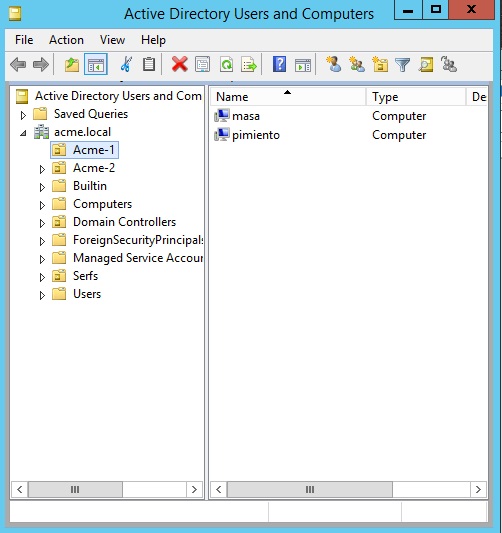
You first set up these OU sub-divisions in Active Directory Users and Computer (below). For each OU, I assigned a subset of the domain’s computers. In my scenario, Acme-1 is associated with the Masa and Pimiento servers, and Acme-2 is associated with Taco, the domain controller.
I also had to remember to create Active Directory groups that will be associated with each of these OUs — Acme-IT-1 and Acme-IT-2.
Now when I’m back in the Group Management Console, these OUs show up under the Acme domain (below). I added a Restricted Groups policy under each OU, making sure that the appropriate AD groups were used.
It’s simpler than it sounds. In short: I’m enabling members of Acme-IT-1 to be an Administrator for Masa and Pimiento, and Acme-IT-2 members for Taco.
We’ll finish up this incredibly exciting topic in the next post and, as always, I’ll have a few closing thoughts. In the meantime, take a few aspirins for getting this far in the series.
What should I do now?
Below are three ways you can continue your journey to reduce data risk at your company:
Schedule a demo with us to see Varonis in action. We'll personalize the session to your org's data security needs and answer any questions.
See a sample of our Data Risk Assessment and learn the risks that could be lingering in your environment. Varonis' DRA is completely free and offers a clear path to automated remediation.
Follow us on LinkedIn, YouTube, and X (Twitter) for bite-sized insights on all things data security, including DSPM, threat detection, AI security, and more.