Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) is an open standard that allows identity providers (IdP) to pass authorization credentials to service providers (SP). What that jargon means is that you can use one set of credentials to log into many different websites. It’s much simpler to manage one login per user than it is to manage separate logins to email, customer relationship management (CRM) software, Active Directory, etc.
SAML transactions use Extensible Markup Language (XML) for standardized communications between the identity provider and service providers. SAML is the link between the authentication of a user’s identity and the authorization to use a service.
Get the Free Pentesting Active
Directory Environments e-book
The OASIS Consortium approved SAML 2.0 in 2005. The standard changed significantly from 1.1, so much so that the versions are incompatible. SAML adoption allows IT shops to use software as a service (SaaS) solutions while maintaining a secure federated identity management system.
SAML enables Single-Sign On (SSO), a term that means users can log in once, and those same credentials can be reused to log into other service providers.
What is SAML Used For?
SAML simplifies federated authentication and authorization processes for users, Identity providers, and service providers. SAML provides a solution to allow your identity provider and service providers to exist separately from each other, which centralizes user management and provides access to SaaS solutions.
SAML implements a secure method of passing user authentications and authorizations between the identity provider and service providers. When a user logs into a SAML enabled application, the service provider requests authorization from the appropriate identity provider. The identity provider authenticates the user’s credentials and then returns the authorization for the user to the service provider, and the user is now able to use the application.
SAML authentication is the process of verifying the user’s identity and credentials (password, two-factor authentication, etc.). SAML authorization tells the service provider what access to grant the authenticated user.
What is a SAML Provider?
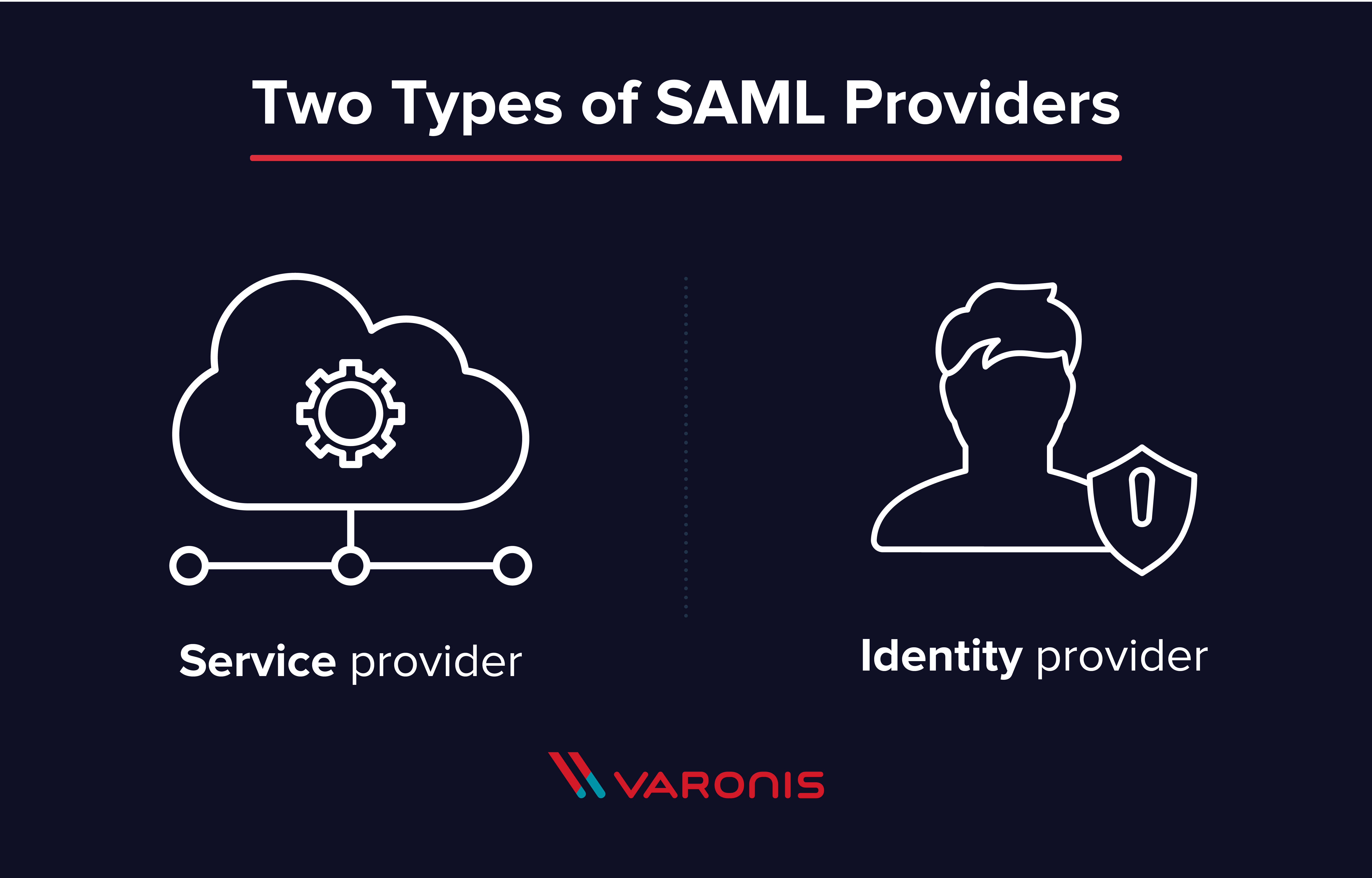
A SAML provider is a system that helps a user access a service they need. There are two primary types of SAML providers, service provider, and identity provider.
A service provider needs the authentication from the identity provider to grant authorization to the user.
An identity provider performs the authentication that the end user is who they say they are and sends that data to the service provider along with the user’s access rights for the service.
Microsoft Active Directory or Azure are common identity providers. Salesforce and other CRM solutions are usually service providers, in that they depend on an identity provider for user authentication.
What is a SAML Assertion?
A SAML Assertion is the XML document that the identity provider sends to the service provider that contains the user authorization. There are three different types of SAML Assertions – authentication, attribute, and authorization decision.
- Authentication assertions prove identification of the user and provide the time the user logged in and what method of authentication they used (I.e., Kerberos, 2 factor, etc.)
- The attribution assertion passes the SAML attributes to the service provider – SAML attributes are specific pieces of data that provide information about the user.
- An authorization decision assertion says if the user is authorized to use the service or if the identify provider denied their request due to a password failure or lack of rights to the service.
How Does SAML Work?
SAML works by passing information about users, logins, and attributes between the identity provider and service providers. Each user logs in once to Single Sign On with the identify provider, and then the identify provider can pass SAML attributes to the service provider when the user attempts to access those services. The service provider requests the authorization and authentication from the identify provider. Since both of those systems speak the same language – SAML – the user only needs to log in once.
Each identity provider and service provider need to agree upon the configuration for SAML. Both ends need to have the exact configuration for the SAML authentication to work.
SAML Example
- Frodo (user) logs into SSO first thing in the morning.
- Frodo then tries to open the webpage to his CRM.
- The CRM – the service provider – checks Frodo’s credentials with the identity provider.
- The identity provider sends authorization and authentication messages back to the service provider, which allows Frodo to log into the CRM.
- Frodo can use the CRM and get work done.
“Need 8 volunteers for a tough project…”
SAML vs. OAuth
OAuth is a slightly newer standard that was co-developed by Google and Twitter to enable streamlined internet logins. OAuth uses a similar methodology as SAML to share login information. SAML provides more control to enterprises to keep their SSO logins more secure, whereas OAuth is better on mobile and uses JSON.
Facebook and Google are two OAuth providers that you might use to log into other internet sites.
SAML Tutorials
A few resources to help research exactly how to implement SAML:
- Configure SAML for Salesforce
- Configure OKTA as SAML IDP
- OneLogin has examples in 5 different programming languages
SAML and SSO are important to any enterprise cybersecurity strategy. Identity management best practices require user accounts to be both limited to only the resources the user needs to do their job and to be audited and managed centrally. By using an SSO solution, you can disable accounts from one system and remove access to all available resources at once, which protects your data from theft.
Varonis protects your core Active Directory services, which in turn helps protect your SSO and SAML systems. Varonis will catch attacks to your AD system long before the attackers can access SSO resources. Get a 1:1 demo to see how Varonis protects Active Directory and your most important data stores from cyberattacks and insider threats.
What should I do now?
Below are three ways you can continue your journey to reduce data risk at your company:
Schedule a demo with us to see Varonis in action. We'll personalize the session to your org's data security needs and answer any questions.
See a sample of our Data Risk Assessment and learn the risks that could be lingering in your environment. Varonis' DRA is completely free and offers a clear path to automated remediation.
Follow us on LinkedIn, YouTube, and X (Twitter) for bite-sized insights on all things data security, including DSPM, threat detection, AI security, and more.










