If you are reading this, you are probably planning a data migration from on-premises data storage to a cloud-based platform or from one cloud platform to another. Data migration can be challenging in the best of times, and it’s crucial to have a secure data migration strategy and execution.
You are not alone. Varonis has helped countless organizations prepare to move from legacy on-premises data in file shares, NAS, and SharePoint to the cloud, and from one cloud environment to another.
This guide is designed to show you how to expedite your migration planning, mitigate risk, and remove the guesswork. Even if you don’t use Varonis, many of the principles in this guide will be helpful in planning your migration.
The better your plan, the more successful your migration will be. A solid planlowers your risk of downtime and ensures your post-migration environment is both secure and easy to maintain.
What is data migration and what does a secure migration look like?
Data migration is the process of moving your data (typically files, emails, and applications) from one infrastructure to another.
Organizations often migrate to the cloud because of the decreased management overhead and flexibility. In the cloud, you can expand or contract their storage requirements with the click of a button rather than purchasing and decommissioning physical servers in a data center.
Many businesses also elect for a hybrid cloud approach: some data stays on-premises, and some moves to the cloud—a decision usually based on data sensitivity or security policy.
In addition, most organizations today are multi-cloud, and moving data from one cloud environment to another is increasingly common, whether to save costs or because a specific use case requires it.
Cloud migration strategy considerations
Migrating data quickly and securely falls squarely on IT’s shoulders. Unfortunately, it can be downright nerve-wracking to move data with little or no downtime, ensure all data is migrated to the correct location, and is accessible to the right people (and only the right people) when it gets there.
Here are some key considerations when planning a migration:
- What data should or shouldn’t be migrated? By excluding stale or obsolete data you can save on storage costs, simplify your migration, and reduce your risk.
- How should sensitive data be handled? Many privacy regulations require specific safeguards for personally identifiable information. Also, any critical data, such as contracts or intellectual property, should be treated with extra care.
- How do I ensure the right users have access once migrated? You don’t want to accidentally cut users off from the data they need to do their job. On the other hand, you have to ensure you don’t unintentionally open up access to people who don’t need it – creating risk of exposure and leakage.
Cloud migration best practices and step-by-step plan

It’s difficult to build a one-size-fits-all checklist that works for all cloud migrations, but this step-by-step guide can serve as a strong foundation. It’s the process we’ve used to guide countless customer migrations.
- Inventory and understand your existing data estate
- Eliminate stale data from your migration scope
- Apply a classification taxonomy to determine the migration scope
- Remediate excessive access to in-scope data
- Assign data owners to sensitive data
- Perform entitlement reviews to further eliminate excessive access
- Review regulations and data security policies
- Understand how Varonis helps protect migrated data
Varonis gave us so much visibility into our network. It’s incredible. We were able to clean up files that we wouldn’t have even known existed, and it definitely aided with PCI compliance.
Senior Manager, Information Security and Compliance at a top U.S. Airline.
1. Inventory and understand your existing data estate
One of the biggest IT challenges, even if you’re not planning a massive cloud migration, is gaining full visibility into your data. Migration projects require a clear and accurate understanding of the nature of your data —the size, relevance, sensitivity, and risk profile.
Most organizations don’t realize just how much dark data they have prior to installing Varonis. Many discover databases, SharePoint sites, Exchange mailboxes, snapshots, public folders, and file shares they didn’t know existed—sometimes with toxic and overexposed regulated information (GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA, etc.).
Varonis automatically discovers sensitive data like PII, PCI, PHI, passwords, tokens, and more across cloud apps and infrastructure, on-prem file shares, and hybrid NAS devices.
Varonis automatically discovers sensitive data like PII, PCI, PHI, passwords, tokens, and more across cloud apps and infrastructure, on-prem file shares, and hybrid NAS devices.
Building a complete and accurate inventory, establishing a classification taxonomy, and prioritizing data sets are essential steps for a successful migration. Varonis gives you the visibility required to take these steps without heaps of manual work and without relying solely on painstakingly surveying end-users.
Explore your unstructured data interactively
Varonis helps you get a picture of your data across disparate systems.
Varonis provides a live representation of your data estate in an interactive view with context about data sensitivity, size, content type, activity, and more.
Varonis provides a unified view across on-premises and cloud data stores, making it easy to look at data and answer questions like:
- Who has access?
- Is the content sensitive?
- Is it being used?
- Is it over-exposed?
In addition, because Varonis provides a bi-directional, you can also answer questions from the user or group perspective, like:
- What data can they access?
- How did they get that access?
- What are they doing with that access?
- Do they need it anymore?
Varonis provides a bidirectional view of data access, making it easy to understand who has access to what data.
Varonis provides a bidirectional view of data access, making it easy to understand who has access to what data.
Migration decisions guided by data
In addition to the interactive work area, Varonis has a suite of reports designed to help you analyze your data estate ahead of your migration.
Varonis reports can help you answer migration questions such as:
- Which data sets are most active and will take serious coordination to migrate?
- Which department shares are candidates to migrate first?
- Which servers contain users’ home drives?
What about the data I don’t even know about?
Varonis also helps you uncover data that you may not even know existed. Shadow data, like databases or Sharepoint sites, often fly under the radar, unnoticed by IT teams. Varonis automatically identifies whether resources contain sensitive data and quickly sees where they are exposed to risk – even if you weren’t aware of the data’s existence.
Varonis surfaces sensitive data that is easily lost, forgotten, or misplaced like database backups and dumps in S3 buckets.
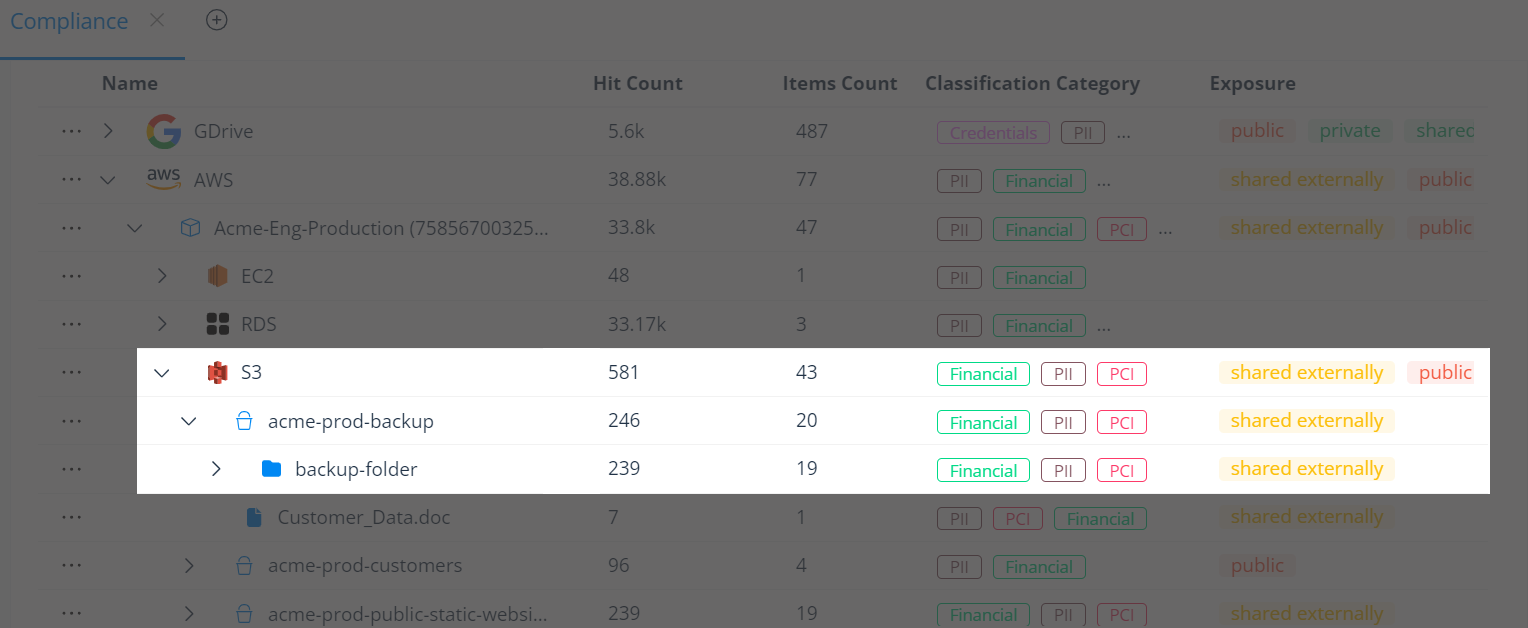
Varonis surfaces sensitive data that is easily lost, forgotten, or misplaced like database backups and dumps in S3 buckets.
2. Eliminate stale data from your migration scope
Because Varonis is actively monitoring all user activity on data — every file open, move, rename, modify, delete — we can confidently identify stale data thatcan be excluded from your migration scope, archived, or deleted.
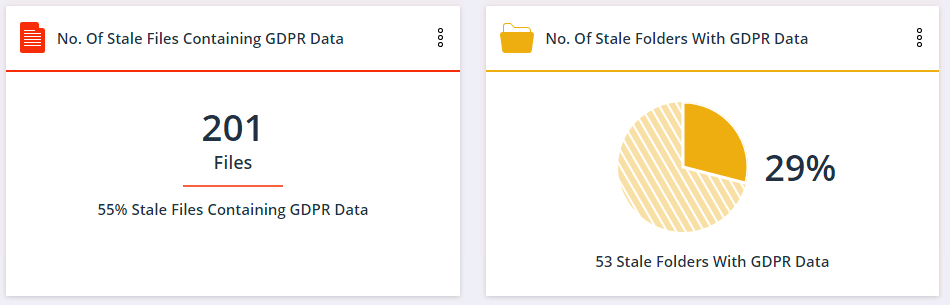
A quick snapshot of stale data per server is available in the KPI dashboards:
You can drill down and see the trend over time, which can be helpful to measure the progress of stale data removal efforts.
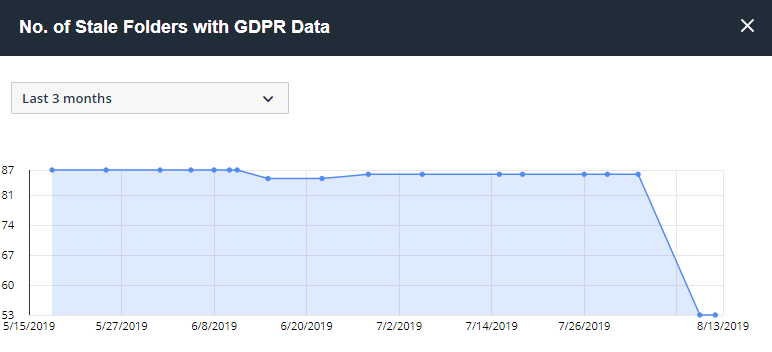
However, most users will want an exportable report of stale data across their entire environment. Varonis has a set of reports to help with that.
Report 7.b.01 Inactive Directories by Size will come in handy. The results of the stale data report can be exported to CSV or other formats and fed into another system for action. Once you’ve identified stale data, you can use Varonis’ built-in flags and tags to mark the data as stale and stage it for automatic archival or removal using a policy in Data Transport Engine.
3. Apply a classification taxonomy to determine migration scope
It’s important to determine what sensitive data — if any — you will migrate and create controls around that data to prevent data breaches. Varonis classifies data for PCI, GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA, and many more regulations out-of-the-box, at a petabyte scale.
You can also import classification results from other products, such as DLP, and configure custom classification rules to discover intellectual property (IP) and other unique business information.
Varonis automatically detects changes to files and re-scans them, which is more efficient than examining every single file daily for changes in its modification timestamp.
Once you know your data, you can start making decisions on security and retention policies.
4. Remediate Excessive Access to In-Scope Data
One of the biggest challenges in all of data security, regardless of where data lives, is to visualize and remediate overexposed sensitive data. On average, employees have access to more than 17 million files, far more than is necessary and 22% of all company data is exposed to everyone in the company.
We suggest customers remediate excessive access prior to migration.
Varonis has the unique ability to eliminate unnecessary permissions at scale. We leverage a powerful forensics layer to understand when access is no longer needed. Instead of opening a ticket for your team to address manually, we fix problems at the source, automatically.
5. Assign data owners to sensitive data
Next, it’s important to understand who the owner of the data should be. Data owners review who has access to information and t and make decisions on what data people should and shouldn’t be using based on business context.
Varonis’ algorithms are very good at determining who should and shouldn’t have access to data. Assigning data owners to critical data sets is an internal process that takes and understanding of the data and who best understands it in your organization.
6. Perform entitlement reviews to further eliminate excessive access
Once data owners are established, force an entitlement review pre-migration to ensure that they weed out excess access that your automated remediation didn’t tackle.
Varonis makes it easy for data owners to review and revoke access via entitlement reviews, inspect usage of their data, and approve/deny incoming access control requests.
7. Review regulations and data security policies
Your organization’s security policies and the regulations your data is subject to will often dictate what to migrate and how that data should be handled.
Varonis comes with ready-made remediation policies that you can customize for your organization. You define the guardrails, and our automation will do the rest. Customize based on sensitivity, staleness, location, link type, and regulatory requirements.
How Varonis helps protect data once it’s migrated
Once your data is migrated, it’s essential to ensure that it is secure to prevent breaches and maintain compliance. Varonis provides the industry’s leading Unified Data Security Platform, enabling you to discover and secure sensitive data automatically, wherever it lives. We do this in three ways:
- Deep visibility: We collect more information on the data than any other solution, including sensitivity, permissions, and activity. This provides you with a complete understanding of exposure and risk, whether your data is in the cloud, on-prem, multi-cloud or hybrid environments.
- Automated remediation: Once we have identified exposures, Varonis can automatically fix the underlying issues, including revoking excessive access and fixing labels. We take the burden of addressing risky permissions, misconfigurations, and exposure off your plate.
- Proactive threat detection: Even if you are doing everything right, bad actors can still get in and target your data. We use automated threat models and have a dedicated team monitoring for abnormal threats, like ransomware, to protect against ongoing threats.
How Saia migrated to the cloud with Varonis
With a mission to migrate to the cloud, Julia Bruce, Identity and Data Governance Manager at Saia, and her team knew they needed to clean up and review 20 years' worth of legacy data before they made the move.
With Varonis, Saia gained visibility into where all their sensitive data is located, who has access to it, who isn't using it, and have trusted recommendations on how to secure crucial information going forward.
"With a lot of other tools, there's gonna be a ton of time that you'll invest tuning it to make sure that a Social Security number is really a Social Security number. But with Varonis, you don't have to do that," Julia said. Watch the full story with the link above.
Interested in migrating to the cloud or to another cloud?
Get started with our free Data Risk Assessment. In less than 24 hours, you’ll have a clear, risk-based view of the data that matters most and a clear path to automated remediation.
What should I do now?
Below are three ways you can continue your journey to reduce data risk at your company:
Schedule a demo with us to see Varonis in action. We'll personalize the session to your org's data security needs and answer any questions.
See a sample of our Data Risk Assessment and learn the risks that could be lingering in your environment. Varonis' DRA is completely free and offers a clear path to automated remediation.
Follow us on LinkedIn, YouTube, and X (Twitter) for bite-sized insights on all things data security, including DSPM, threat detection, AI security, and more.







-1.png)

