The Risk Management Framework (RMF) is a set of criteria that dictates how the United States government's IT systems must be architected, secured, and monitored.
Originally developed by the Department of Defense (DoD), the RMF was adopted by the rest of the US federal information systems in 2010. Today, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) maintains NIST and provides a solid foundation for any data security strategy.
The RMF builds on several previous risk management frameworks and includes several independent processes and systems. It requires that organizations implement secure data governance systems and perform threat modeling to identify cyber risk areas.
In this guide, you'll learn:
- What comprises the RMF?
- Components of the RMF
- 6 Steps of the RMF
- Benefits of the RMF for organizations
- The benefits of the RMF for businesses
What comprises the Risk Management Framework?
The general concept of “risk management” and the “risk management framework” might appear to be quite similar, but it is important to understand the distinction between the two. The risk management process is specifically detailed by NIST in several subsidiary frameworks.
The most important is the elegantly titled “NIST SP 800-37 Rev.1” which defines the RMF as a 6-step process to architect and engineer a data security process for new IT systems, and suggests best practices and procedures each federal agency must follow when enabling a new system.
In addition to the primary document SP 800-37, the RMF uses supplemental documents SP 800-30, SP 800-53, SP 800-53A, and SP 800-137:
- NIST SP 800-30, or Guide for Conducting Risk Assessments, provides an overview of how risk management fits into the system development life cycle (SDLC) and describes how to conduct risk assessments and how to mitigate risks.
- NIST SP 800-37 discusses the risk management framework itself and contains much of the information we’ll cover in the remainder of this guide.
- NIST SP 800-39, or Managing Information Security Risk, defines the multi-tiered, organization-wide approach to risk management crucial for reaching compliance with the RMF.
Components of the Risk Management Framework
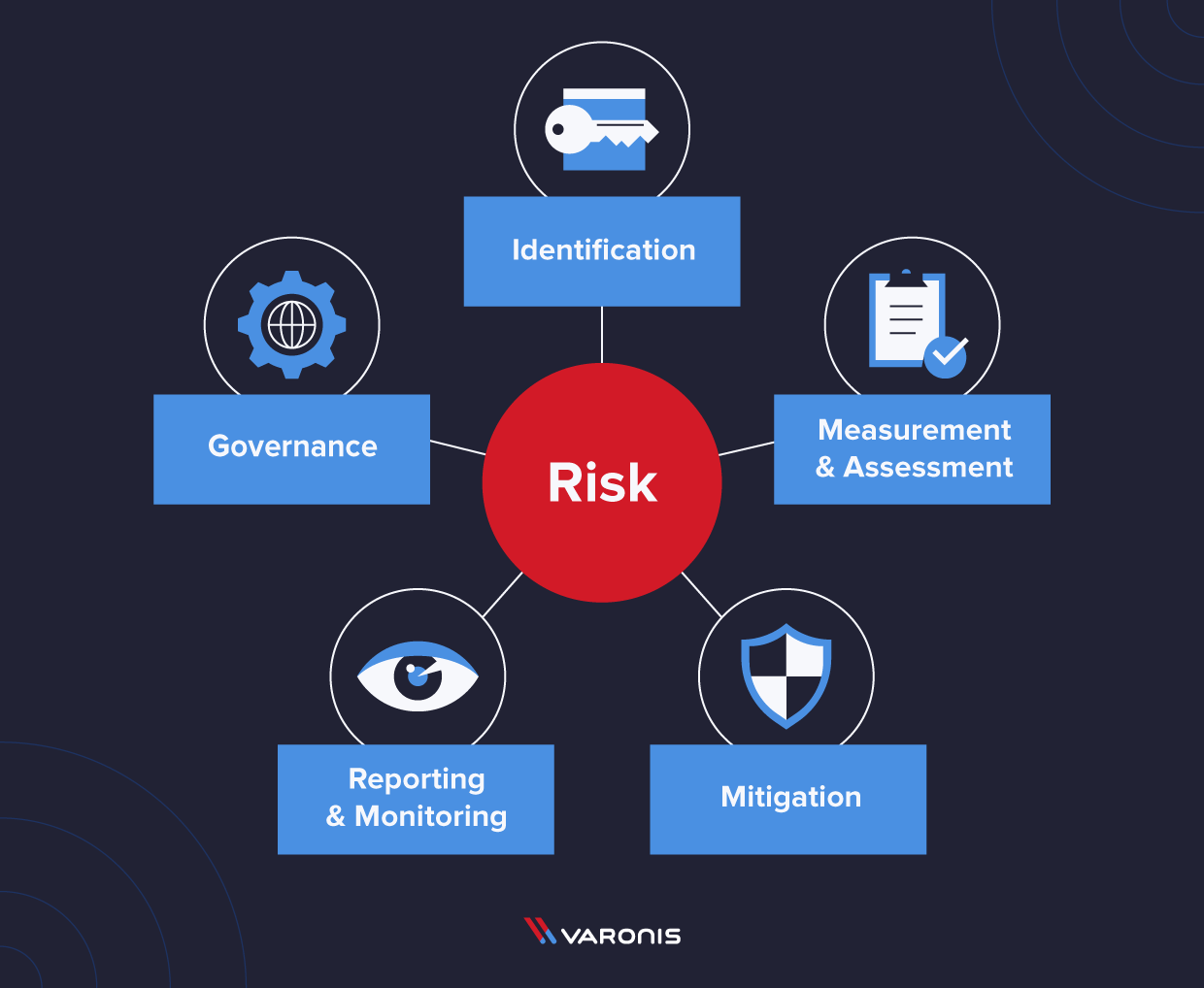
When getting started with the RMF, it can be useful to break the risk management requirements into different categories. These categories provide a way of working toward an effective risk management system, from identifying the most critical risks you face to how you will mitigate them.
Risk identification
The first, and most important, part of the RMF is to perform risk identification. NIST says, “the typical risk factors include threat, vulnerability, impact, likelihood, and predisposing condition.” During this step, you will brainstorm all the possible risks you can imagine across all of your systems and then prioritize them using different factors:
- Threats are events that could potentially harm the organization by intrusion, destruction, or disclosure.
- Vulnerabilities are weaknesses in the IT systems, security, procedures, and controls that can be exploited by bad actors (internal or external).
- Impact is a measurement of how severe the harm to the organization would be if a particular vulnerability or threat is compromised.
- Likelihood is a measurement of the risk factor based on the probability of an attack on a specific vulnerability.
- Predisposing conditions are a specific factor inside the organization that either increases or decreases the impact or likelihood that a vulnerability will come into play.
Risk measurement and assessment
Once you have identified the threats, vulnerabilities, impact, likelihood, and predisposing conditions, you can calculate and rank the risks your organization needs to address.
Risk mitigation
Organizations take the previous ranked list and start to figure out how to mitigate the threats from the greatest to the least. At some point in the list, the organization can decide that risks below this level are not worth addressing, either because there is little likelihood of that threat getting exploited, or if there are too many greater threats to manage immediately to fit the low threats into the work plan.
Risk reporting and monitoring
The RMF requires that organizations maintain a list of known risks and monitor known risks for compliance with the policies. Statistics on data breaches indicate that many companies still do not report all of the successful attacks they are exposed to, which could impact their peers.
Risk governance
Finally, all of the steps above should be codified into a risk governance system.
The 6 steps of the Risk Management Framework (RMF)
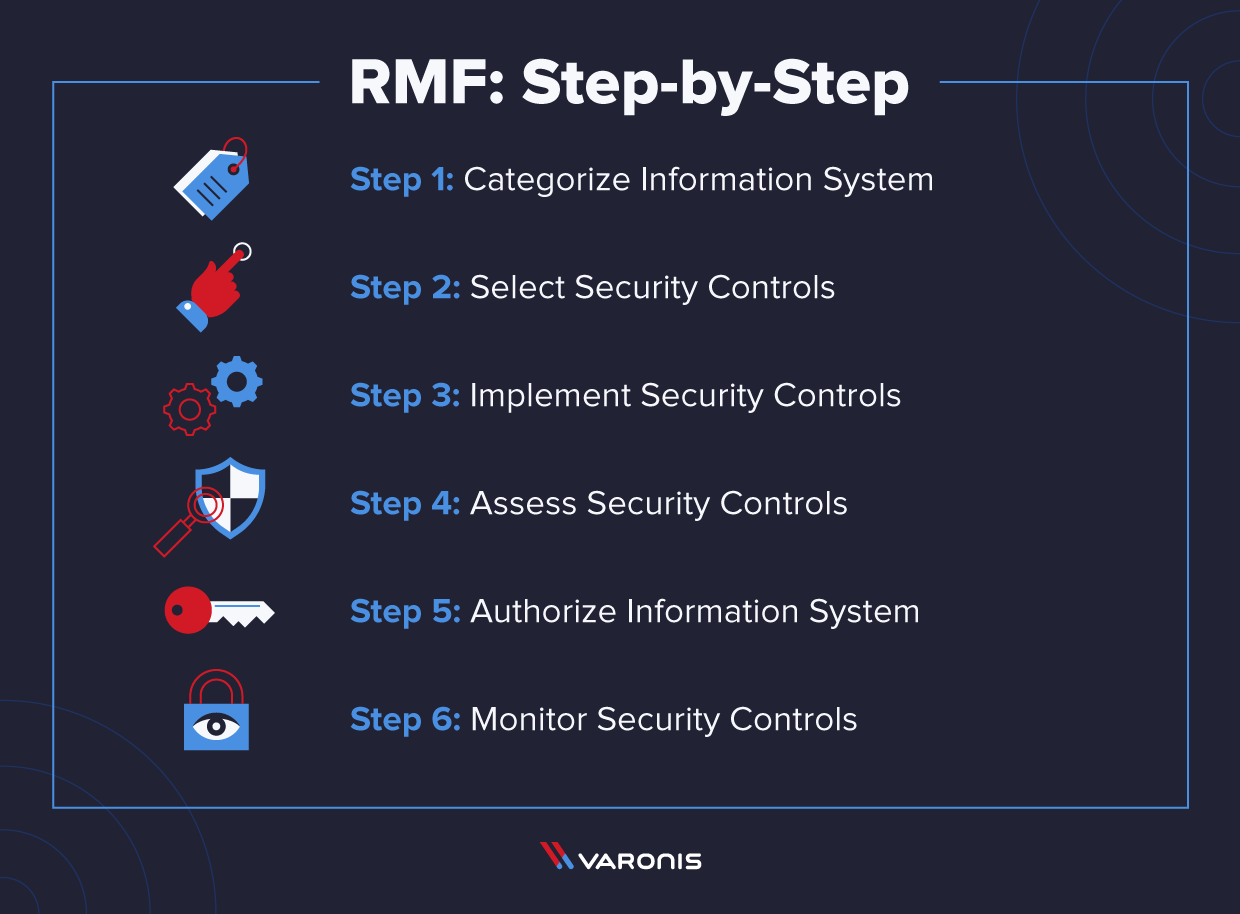
At the broadest level, RMF requires companies to identify which system and data risks they are exposed to and implement reasonable measures to mitigate them. The RMF breaks down these objectives into six interconnected but separate stages.
1. Categorize information systems
- Use NIST standards to categorize information and systems so you can provide an accurate risk assessment of those systems.
- NIST tells you what kinds of systems and information you should include, including what level of security you need to implement based on the categorization.
References: FIPS Publication 199, Standards for Security Categorization of Federal Information and Information Systems; Special Publication 800-60 Rev. 1 (Volume 1, Volume 2), Guide for Mapping Types of Information and Information Systems to Security Categorie
2. Select security controls
Select the appropriate security controls from the NIST publication 800-53 to “facilitate a more consistent, comparable, and repeatable approach for selecting and specifying security controls for systems.”
References: Special Publication 800-53 Security and Privacy Controls for Federal Information Systems and Organizations ed. note the updated version of 800-53 goes into effect on September 23, 2021. Stay tuned for details.
3. Implement security controls
Put the controls you selected in the previous step in place and document all the processes and procedures you need to maintain their operation.
References: Multiple publications provide best practices to implement security controls. Check out this page to search for them.
4. Assess security controls
Make sure the security controls you implemented are working the way they need to so you can limit the risks to your operation and data.
5. Authorize information systems
If the security controls are effectively reducing organizational risk, the system can be authorized.
References: Special Publication 800-37 Rev. 2 Risk Management Framework for Information Systems and Organizations: A System Life Cycle Approach for Security and Privacy
6. Monitor security controls
Continuously monitor and evaluate security controls to ensure they remain effective throughout system operation. Update controls as needed, document all changes, perform regular impact analyses, and report the control status to designated officials.
References: Special Publication 800-37 Rev. 2 Risk Management Framework for Information Systems and Organizations: A System Life Cycle Approach for Security and Privacy
How an effective Risk Management Framework benefits your business
Though the RMF is a requirement for businesses working with the US government, implementing an effective risk management system can benefit all organizations. The ultimate goal of working toward RMF compliance is the creation of a data and asset governance system that will provide full-spectrum protection against all the cyber risks you face.
More specifically, developing a practical risk management framework will provide a company with several specific benefits:
- Asset protection: A risk management framework identifies threats to your data and assets. This ensures your most critical business resources remain secure.
- Reputation management: It helps detect security gaps and reduce the impact of breaches. This protects your brand in a market where consumer trust is vital.
- IP protection: Risk frameworks safeguard your intellectual property from theft or misuse. This preserves your competitive edge and avoids legal exposure.
- Competitor analysis: Cataloging risks reveals valuable insights about your market landscape.This knowledge can lead to strategic advantages over competitors.
Simplify Risk Management Framework (RMF) compliance with Varonis
Varonis helps you meet the core pillars of the Risk Management Framework (RMF): identify, protect, and monitor—with automation, precision, and speed.
- Identify at-risk data and access:
- Instantly locate sensitive data across file systems, map user and group permissions, and surface excessive or risky access.
- Know exactly where your sensitive data lives and who can access it, which is essential for risk assessments under NIST SP 800-53.
- Protect your environment with least-privilege enforcement:
- Monitor and detect threats in real time:
- Analyze billions of events across data access, VPN, DNS, proxy, and AD to detect insider threats, malware, ransomware, and more.
- Machine learning builds behavioral baselines and flags anomalies—so you can stop threats before they become breaches.
RMF compliance doesn’t have to be a manual, complex process. With Varonis, you can automate much of the work and gain lasting improvements to security posture, operational efficiency, and audit readiness.
Learn how Varonis can help you meet NIST SP 800-37 and streamline your path to RMF compliance.
FAQs for Risk Management Framework (RMF)
What is the Risk Management Framework (RMF)?
The Risk Management Framework (RMF) is a set of criteria that dictate how United States government IT systems must be architected, secured, and monitored. Originally developed by the Department of Defense, the RMF was adopted by all US federal information systems in 2010 and is now maintained by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). The framework provides a structured process for identifying, assessing, and managing security risks across information systems.
Who needs to follow the RMF?
All U.S. federal agencies and contractors working with federal information systems must comply with RMF requirements.
What are the 6 steps of the Risk Management Framework?
The RMF consists of six interconnected steps:
- Categorize information systems. Classify information and systems according to risk levels
- Select security controls. Choose appropriate security measures based on NIST guidelines
- Implement security controls. Put selected controls in place and document procedures
- Assess security controls. Verify controls are working effectively
- Authorize information systems. Formally approve systems when controls adequately reduce risk
- Monitor security controls. Continuously assess effectiveness and make necessary adjustments.
Each step builds upon the previous one to create a comprehensive security approach.
What are the main components of risk management?
Risk management under the RMF comprises five key components.
- Risk identification: Organizations identify threats, vulnerabilities, impacts, and likelihood of risks.
- Risk measurement and assessment: Calculating and ranking identified risks.
- Risk mitigation: Developing strategies to address risks from highest to lowest priority.
- Risk reporting and monitoring:.= Maintaining documentation and ongoing surveillance of known risks.
- Risk governance: Codifying all these processes into formal policies and procedures.
How can the Risk Management Framework benefit businesses?
While the RMF is mandatory for government contractors, implementing it provides several benefits for any business. It enhances asset protection by prioritizing security measures for critical data and systems. The framework helps with reputation management by reducing the likelihood and impact of breaches that could damage public trust.
RMF implementation protects intellectual property from theft, preserving competitive advantages. Additionally, the process of cataloging risks provides valuable market intelligence that can inform strategic business decisions and create competitive advantages.
What should I do now?
Below are three ways you can continue your journey to reduce data risk at your company:
Schedule a demo with us to see Varonis in action. We'll personalize the session to your org's data security needs and answer any questions.
See a sample of our Data Risk Assessment and learn the risks that could be lingering in your environment. Varonis' DRA is completely free and offers a clear path to automated remediation.
Follow us on LinkedIn, YouTube, and X (Twitter) for bite-sized insights on all things data security, including DSPM, threat detection, AI security, and more.


-1.png)




