Varonis Threat Labs is shining a spotlight on a decade-old vulnerability that opens the door to URL spoofing.
By exploiting how browsers handle Right-to-Left (RTL) and Left-to-Right (LTR) scripts, attackers can craft URLs that appear trustworthy but actually lead somewhere else, therefore this method, known as BiDi Swap, can be often abused in phishing attacks.
Past Unicode attacks and spoofing
Before BiDi Swap, several Unicode-based tricks were used to fool both users and browsers into displaying deceptive text or URLs. Two standout examples are:
- Punycode Homograph Attacks: Internationalized Domain Names (IDNs) let websites use non-Latin characters (e.g., Russian “а,” Cyrillic “с,” or Greek “ο”) that look nearly identical to well-known Latin letters. This can create spoofed domains like “аpple.com” or “рayрal.com” with only minor character differences. Browsers convert these for consistent handling (e.g., “xn--something”), but attackers often sneak in visually identical characters, tricking people into believing they’re on a legitimate site.
- RTL Override Exploits: Some attackers embed special Unicode characters (e.g., U+202E) that flip text direction mid-string. This can disguise URL paths, make file extensions look harmless, or reorder text to hide malicious file endings like:
“blafdp.exe” -> “blaexe.pdf”
While these control characters are necessary for handling right-to-left languages properly, they can also mask dangerous content or rearrange the layout, so a site or file name appears safe at a quick glance.
These past attacks set the stage for BiDi Swap by revealing how tiny nuances in text handling can have big security consequences and how ongoing vigilance is needed to prevent these spoofing tricks.
LTR, RTL and BiDi who?
When it comes to text direction, many languages, like English or Spanish, flow left to right (LTR), while others, such as Arabic or Hebrew, go right to left (RTL). This mix can be a challenge for computers, which need to keep everything aligned so text doesn’t become a scrambled mess. That’s where the Bidirectional (Bidi) Algorithm steps in.
Part of the Unicode Standard, Bidi helps computers correctly display LTR and RTL scripts in the same text.
However, while the Bidi Algorithm usually handles domains decently, it struggles with subdomains and URL parameters. This gap means mixed LTR–RTL URLs might not display as intended, creating an open door for mischief.
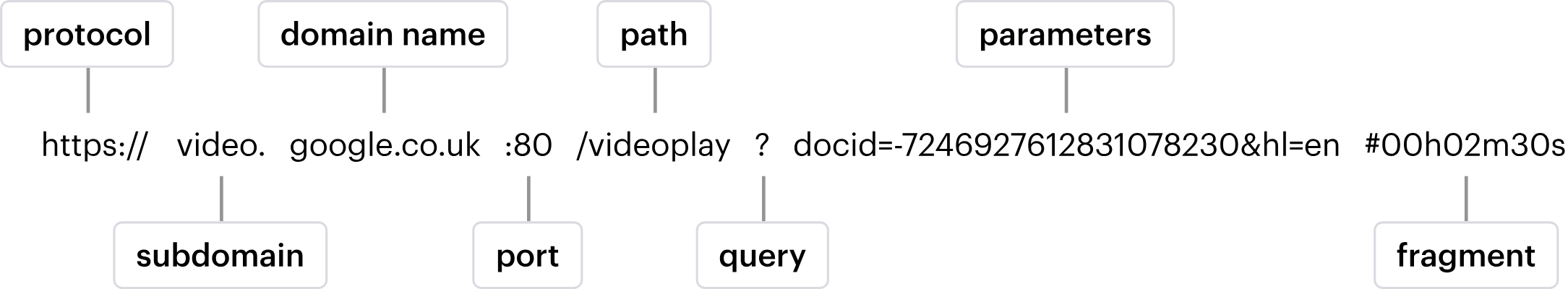
URL structure
Here’s a quick refresher on what a URL is and how it’s structured: A URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is a standardized way to point to resources on the web, and it typically contains several key components:
- Protocol (Scheme): This defines how the resource is accessed, for example “http://” or “https://.”
- Subdomain: An optional part before the main domain (e.g., “www.” in “www.example.com”), which can organize content within larger sites
- Domain: The core part of the address (e.g., “example”)
- Top-Level Domain (TLD): The ending of the domain name (e.g., “.com,” “.org,” “.net”) that often indicates the purpose or geographical location
- Path: The directory or file structure that appears after the domain (e.g., “/blog/posts”)
- Query String/Parameters: Key-value pairs used to pass extra information to the server, usually starting with a question mark (e.g., “?id=123”)
Bidi swap
Let’s start with something simple: a regular right-to-left (RTL) host (domain + TLD) might look like this (Yes, we got a one-letter host):
Now, let’s add a protocol and mix in both RTL and LTR parameters:
Notice how placing parameters on the right quickly becomes confusing. Next, let’s try adding an English parameter that looks like another domain name:
That still doesn’t yield the expected behavior. Now, let’s see what happens when we try to mimic a subdomain:
Combining an LTR subdomain with some RTL parameters:
More payloads
Try it yourself: Change the varonis subdomain to any domain you like and watch the magic happen!
Disclaimer: This site is provided as-is and is intended solely for educational and informational purposes. It demonstrates a proof-of-concept related to browser behavior and potential misuse. The user assumes full responsibility for any use of the code or techniques presented herein, including any consequences that may arise. The authors and maintainers of this site do not endorse or encourage misuse, and no liability is accepted for any actions taken based on this content.
Browser mitigations
Chrome
Bidi Swap has been a known issue in Chrome for over a decade. While Chrome’s “Navigation suggestion for lookalike URLs” feature provides partial protection, our testing shows it only flags certain domains (e.g., “google.com”), letting many others fly under the radar.
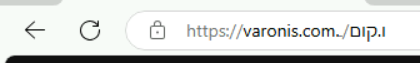
Firefox
Firefox has also recognized this as a longstanding issue. However, rather than relying on suggestions for lookalike URLs, Firefox takes a different UI approach. By highlighting key parts of the domain in the address bar, Firefox makes it easier for users to spot potential spoofs or suspicious links.

Edge
We informed Microsoft and they marked the issue as resolved, but the URL representation seems to remain unchanged.
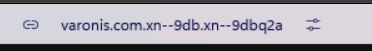
ARC
Arc is no longer developed, but here is an example of a browser that did it right:
Conclusion and recommendations
To combat BiDi Swap, follow these recommendations:
- Awareness is key: Always verify suspicious URLs — especially those that mix scripts or show unexpected patterns
- Push for improvement: Browser developers should refine existing protections like domain highlighting and lookalike detection to close these security gaps
- Educate users and teams: Encourage everyone to hover over links, confirm SSL certificates, and check domain consistency. A few extra seconds can thwart a major security risk.
Discover more from the Varonis Threat Labs team on our blog.
What should I do now?
Below are three ways you can continue your journey to reduce data risk at your company:
Schedule a demo with us to see Varonis in action. We'll personalize the session to your org's data security needs and answer any questions.
See a sample of our Data Risk Assessment and learn the risks that could be lingering in your environment. Varonis' DRA is completely free and offers a clear path to automated remediation.
Follow us on LinkedIn, YouTube, and X (Twitter) for bite-sized insights on all things data security, including DSPM, threat detection, AI security, and more.







